In recent years, the prevalence of technology and artificial intelligence (AI) in our daily lives has dramatically increased.
With the advent of new artificial intelligence platforms, such as ChatGPT, it is expected that technology will have a big impact on the workplace in the coming years. Specifically, technology is predicted to replace jobs like data entry, bookkeeping, or fundamental customer service roles, according to a study from the National Library of Medicine.
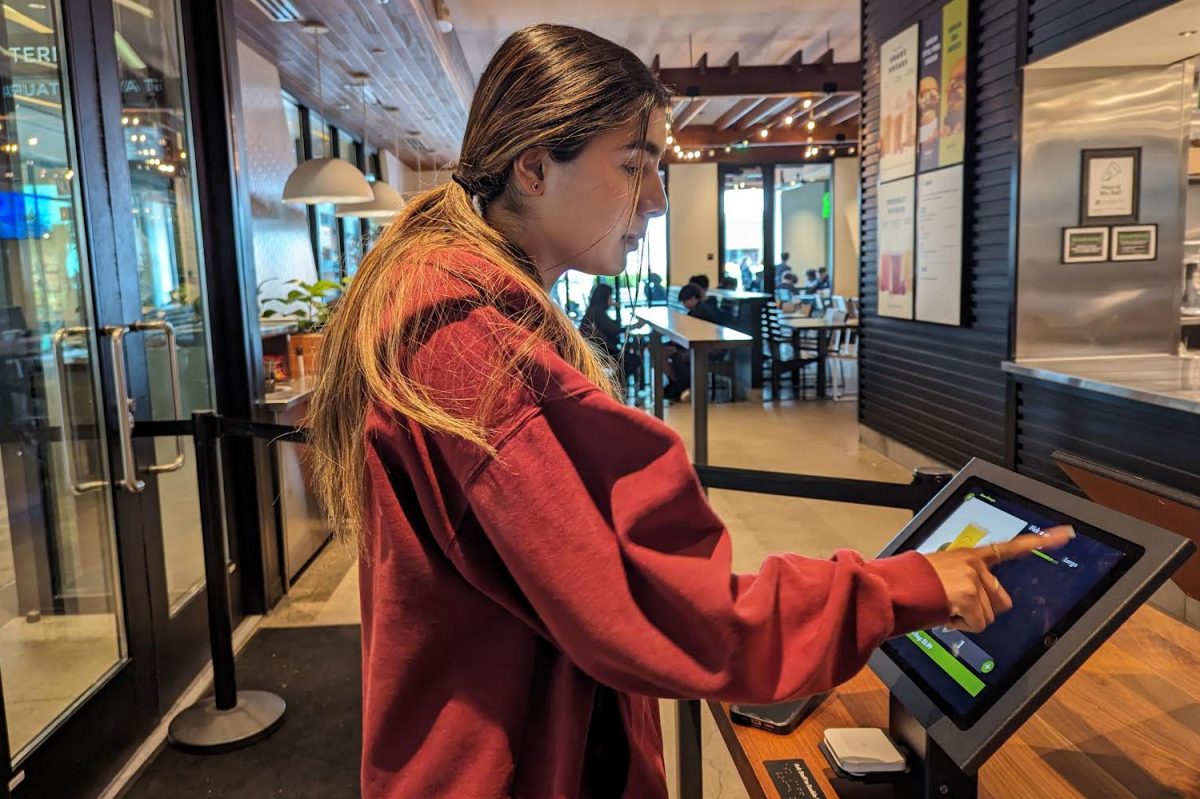
Already, technology has become more popular in many areas of daily life: in grocery stores with self-checkout technology, in fast food restaurants like McDonald’s and Shake Shack, where customers can order from iPads instead of interacting with a cashier, QR code menus at restaurants, or on websites with AI chat support.
While some of these innovations improve efficiency, like increased website support for questions not requiring humans, they also significantly reduce social interaction.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), humans are, by nature, social creatures, and social connections are essential for our survival. Research shows that this can lead to a longer lifespan and better health.
This primarily applies to familial relationships or friendships, but everyday interactions with classmates, coworkers, waiters, customer service personnel, and others can make an impact.
Thus, as many sectors continue switching to technology, and many customer service outlets will be automated in the future, this could have negative social implications.
Humans overall have become less social, especially teenagers, according to an article by the Scientific American.
This decreasing socialization is directly linked to phone and technology usage. In a Pew Research survey in 2018, 45% of teenagers reported they used the Internet almost constantly, which nearly doubled from the 24% reported in 2015.
Additionally, teenagers are overall socializing less than previous generations, according to an article from the National Library of Medicine. The pandemic, combined with excessive phone and social media usage, exacerbated these effects, and teenagers are more likely to spend time at home and simply be on their phones.
It is clear that humans are already facing a lack of social interaction due to increased technology use, so rushing this process by replacing more jobs involving social interaction with technology could be detrimental.
In many areas, we are moving toward entirely automated interactions, which could have significant negative impacts, especially because the socialization of people has already dramatically reduced due to increased time spent on cell phones. Efficiency is important, but not at the expense of socialization.